The increasing rate of bacterial resistance creates a challenging environment for the development of therapies for bacterial infections. Bacterial skin infections are one of the leading manifestations of infectious diseases in the world. Staphylococcus aureus—both Methicillin-resistant (MRSA) and Methicillin-Sensitive (MSSA) strains—is the leading cause of skin and soft tissue infections in the USA. It is the leading cause of hospital-associated (HA) and community-associated (CA) infections worldwide.
IBT Bioservices now offers a validated Staphylococcus aureus skin infection model for investigating the pathogenesis of skin and soft tissue infections and testing the efficacy of antibacterial drug or vaccine candidates. In this BALB/c mouse model, the mice’s backs are shaved prior to intradermal (ID) infection with a predetermined dose of S. aureus USA300. The treatment candidate is administered and the abscess lesion size (visible dermonecrosis) is measured once daily using digital calipers. Lesion area is calculated according to the following formula of an ellipse: A= Length/2 x Width/2 x π (approx. 3.14159). Animals are monitored twice a day for up to 14 days to measure disease severity including weight loss and morbidity.
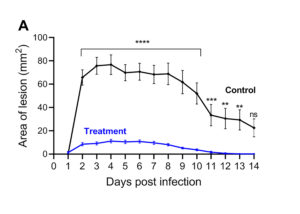
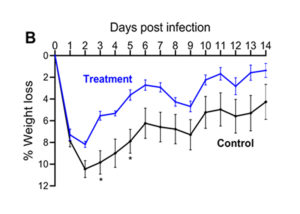
The skin infection model figures above show results from animals that received a test treatment (blue) or a placebo control (black) via intraperitoneal (IP) injection 4 hours prior to infection. The area of lesion (A) and weight loss (B) are measured daily for 14 days post-infection with 1×107 CFU of S. aureus USA300.
At IBT Bioservices we offer a range of discovery tools and testing services to help progress your project toward your developmental milestone and secure your next round of funding. We share your goals of bringing new treatments to market. If you have an antimicrobial candidate you would like to test in this model, contact us.